关注清华的同学可能知道,昨天,“清华大学”公众号发了一篇名为《2018,我们共芳华丨@THUers 致相伴一年的你,请查收这份心意》的推送,内容大概就是,有那么 100 个新年台历礼品要送出去,大家如果想要的话,就扫描小程序。小程序模仿了火车抢票的病毒式营销的模式,要求大家分享到群聊或者朋友圈,让别人给自己加速,加速到 2019 的前 100 名即可填写信息领取奖品。
然后大家就在推送里看到了我。就酱。
这件事情据说策划了有一段时间了,只是因为各种原因一直没有做,最后这个锅就路由到了我的头上。一开始说就是个加速小程序,逻辑很简单,但后来逐渐发现需求越来越多,主要是界面上的,动画上的,还有一些非技术因素的功能,嗯。这其实算是一个不大好的软件工程案例。
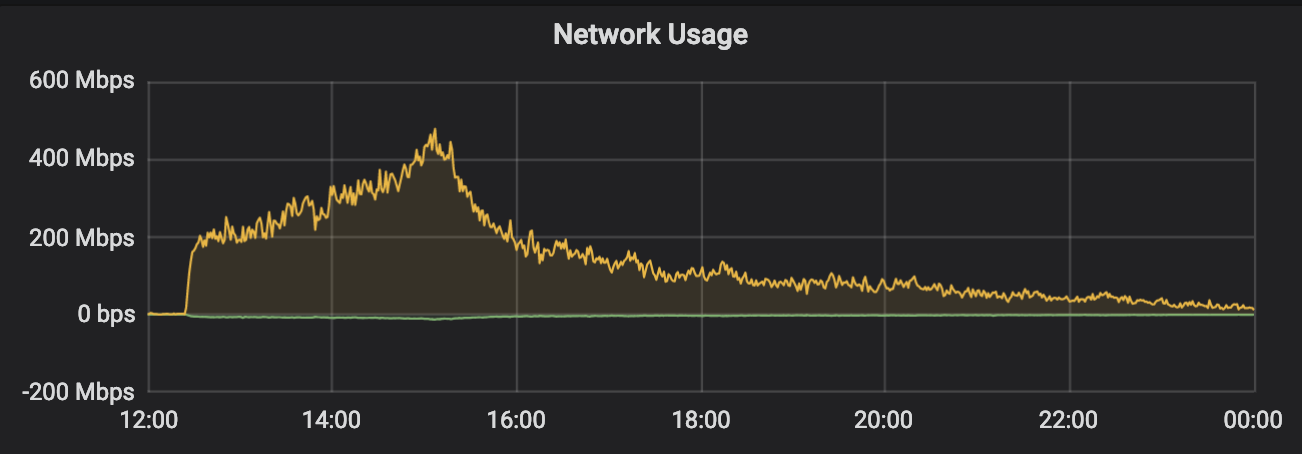
然后就是上线了。大概是昨天(2018-12-27)中午的时候推送发出去,很快流量就开始来了。很快,在朋友圈看到有同学在转发了,也有人反映说,网络有点卡,加载资源有点多。我去机器上用 iftop 看了下,流量大概是 250Mb/s,没打到千兆。我一开始看了下,CPU 和内存占用都良好,以为是网络出口限制的问题,就想着没办法了,就这样吧,扛过去再说。不过,忽然有了转机。
TUNA 技术群里,忽然有人在讨论 SOMAXCONN 的问题,我想到,会不会是有些参数没开够大,导致了性能瓶颈,又受到啊荣的点拨,立马调整了这些变量:
net.core.somaxconn
fs.file-max
net.core.netdev_max_backlog
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog
nginx: worker_rlimit_nofile
nginx: event.worker_connections
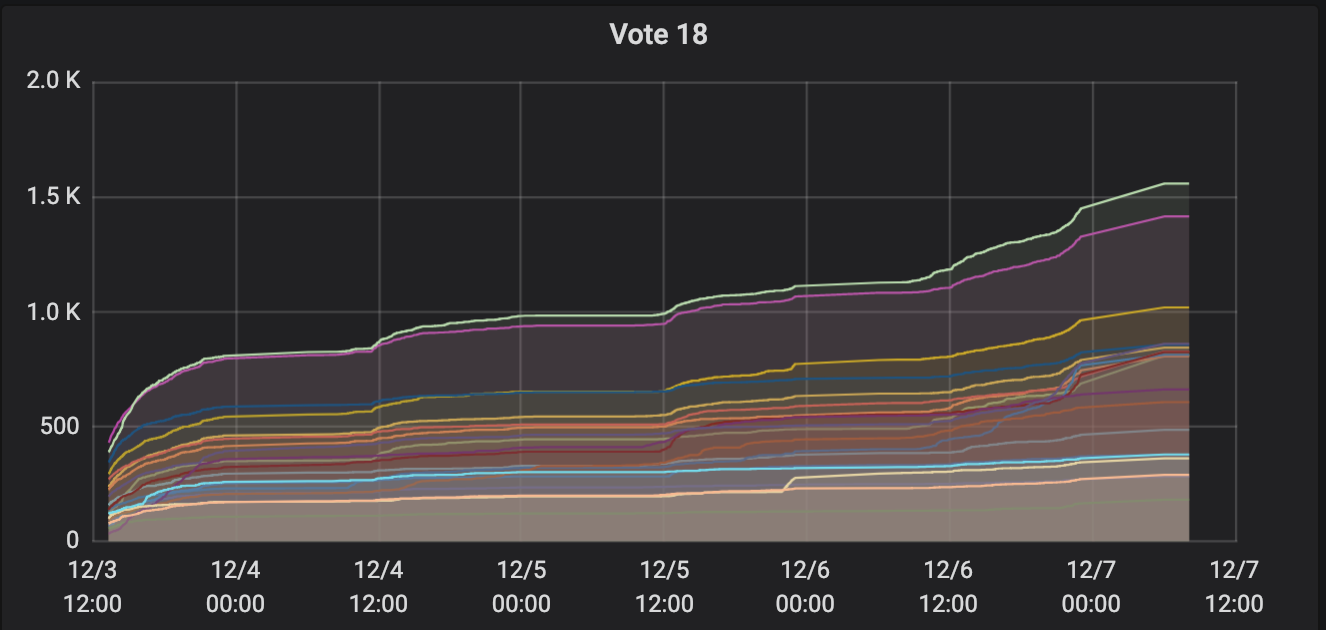
很快带宽从 200Mb/s 左右打到了 400Mb/s 多,在 iftop 中看到的峰值接近 600Mb/s,见下图:
事后回来看,发现配置一套科学的监控系统真的很有用,如 TCP 连接的状态图:
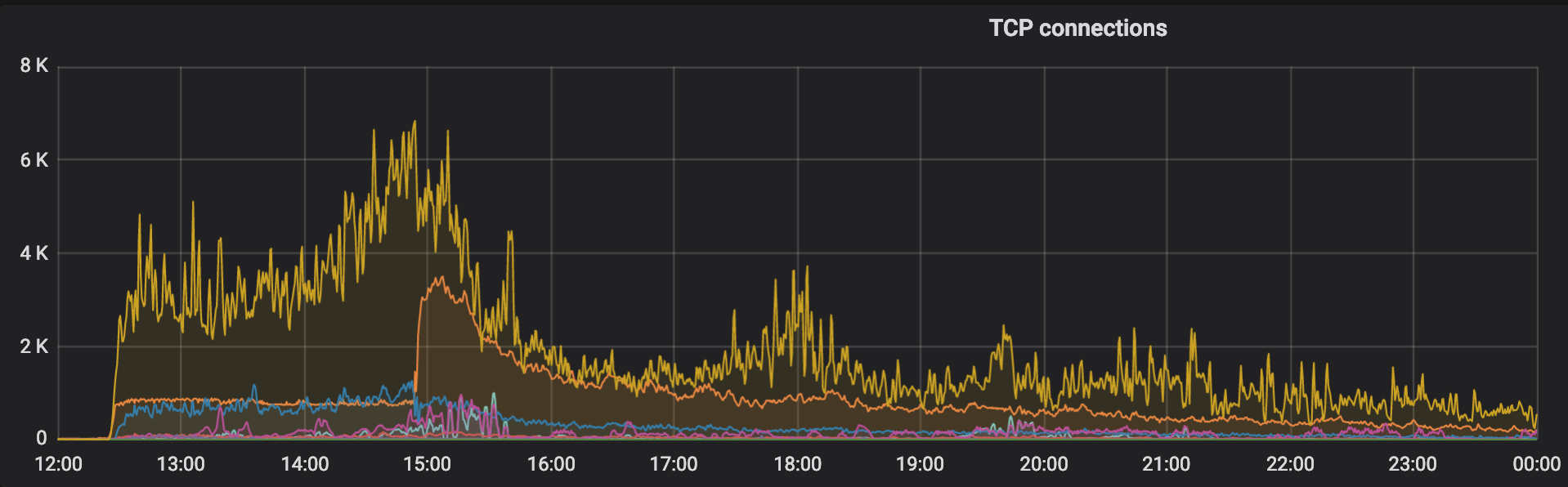
这里最高的黄线代表的是 TIME_WAIT,意味着很多的 TCP 连接都卡在了等待资源上,而一当我修改参数以后,立刻就降了下来,ESTBALISHED 的连接有了显著的提升。这个问题从另一个图也可以明地看出:
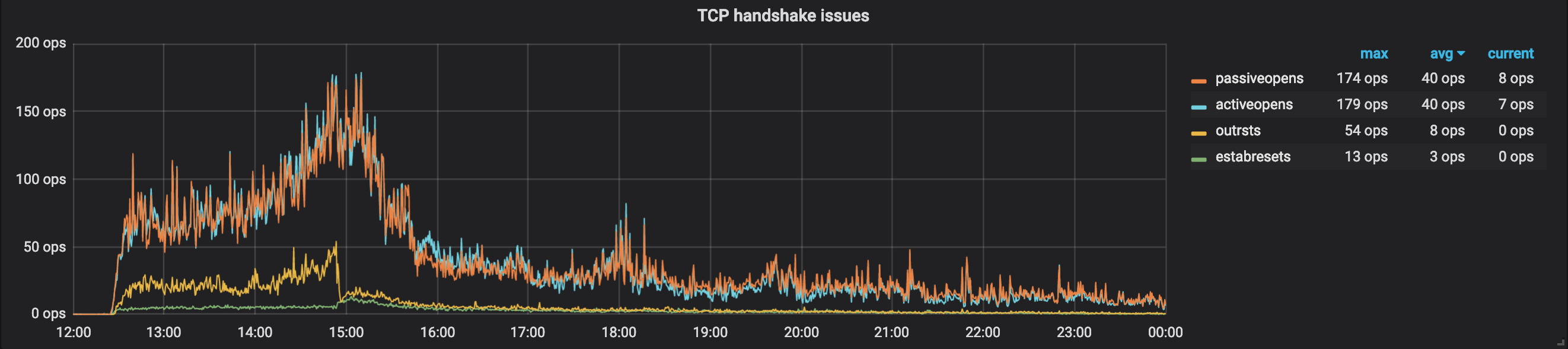
这个图是 TCP Handshake Issues,可以看到无论是 activeopen 还是 passiveopen,都很高,意味着这里无论是发还是收都遇到了问题。而修改参数以后,这些问题立马得到了很好的改善。
其实这些本应该在上线前做好的,但我低估了清华大学的影响力,没有做好相应的准备,还是在优秀的运维人员的指点下得到了较好的效果。
当然了,除了 Grafana+InfluxDB+Telegraf 这一套监控系统,我们也部署了 ElasticSearch+Logstash+Kibana,只不过我们还是用 Grafana 做了 ElasticSearch 的前端了。通过对 Nginx 日志的分析,我们得到了这些关键的数据(从 12-26 12:00 到 12-27 12:00 一天时间):
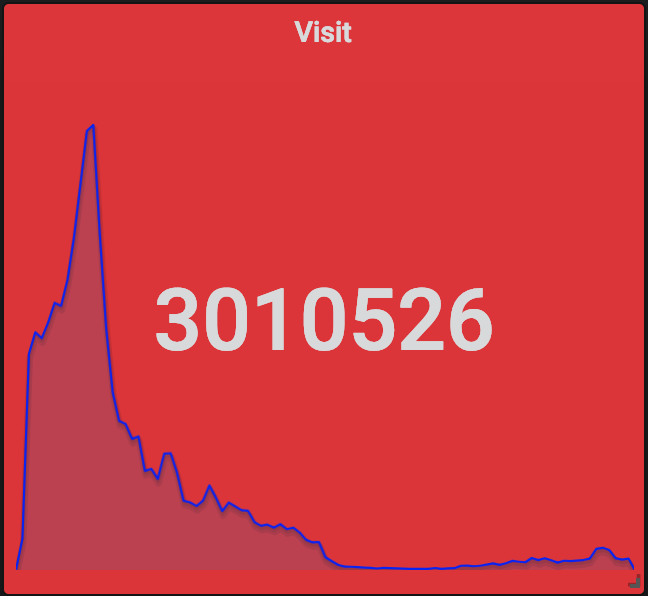
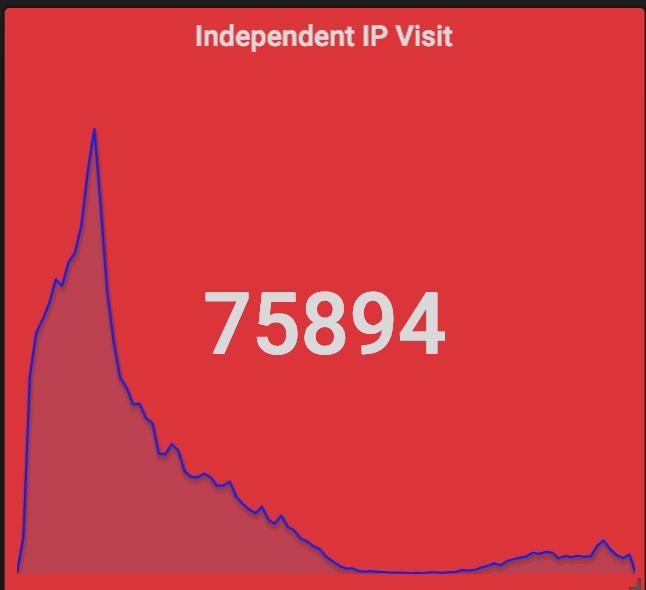
除了这些,还有很多有趣的数据,例如用户里北京的最多,也可以大致地看出各个地方网络和手机的普及程度;用户使用的手机的机型里前几名都是苹果的,从单项占领了排名的前很多位,之后则是华为小米 OPPO 等,但总体上反而是安卓用户更多。
微信小程序官方也提供了一些数据统计可供参考。例如页面的访问次数信息,一共大约有二十多万次,打开小程序有十三万多次,访问人数是五万多,还有女性用户比男性用户多等等。这个时代,有数据确实能够得到许多有价值的判断。
这次学到了很多东西,验证了监控系统的必要性,它能够实时看到服务的运行状态并进行调优,事后也可以回过头来进行进一步的分析和总结。不足的是,遇到大客户量的时候,静态资源就应该用 CDN 服务而不应该自己搭建,成本不高而且用户体验会很好。这次后端在数据库操作都用了原子操作,没有出现大的问题,但如果以后遇到更复杂的需求的时候就没有这么容易了。