Lock Free 数据结构
Treiber Stack
Treiber Stack 是一个 Lock-Free 的 Stack,支持 Push 和 Pop 操作,由 R. Kent Treiber 在 1986 年提出,出现在 Systems Programming: Coping With Parallelism 第 17 页。原文中,它是由汇编编写的:
图中用的是 IBM System/370 指令集,用到的部分汇编指令包括:
LABEL EQU *: 创建一个 LABEL 符号,它的值等于当前的地址,相当于LABEL:语法L REG, MEM:从 MEM 内存读取数据到 REG 寄存器ST REG, MEM:把 REG 寄存器的数据写入到 MEM 内存CS REG1, REG2, MEM:Compare and Swap,把 MEM 内存中的数据和 REG1 进行比较,如果相等,把 REG2 写到 MEM 内存中;如果不相等,把 MEM 内存中的值读取到 REG1 寄存器LTR REG1, REG2:Load Test Register,比较 REG1 和 REG2 的值
翻译成 C++ 代码,它做的事情大概是(参考了 cppreference):
#include <atomic>
#include <optional>
template <class T> struct Node {
T data; // user data
Node<T> *next; // pointer to next node
Node(const T &data) : data(data), next(nullptr) {}
};
template <class T> struct Stack {
// paper: ANCHOR
// head of singly linked list
std::atomic<Node<T> *> head;
Stack() : head(nullptr) {}
// paper: PUTEL
void push(const T &data) {
Node<T> *new_head = new Node<T>(data);
// paper: L R2, ANCHOR
// read current head
Node<T> *cur_head = head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
// paper: ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4)
// link the new list
new_head->next = cur_head;
// paper: CS R2, R4, ANCHOR; ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4) on failure
// atomic swap if head == new_head->next
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: new_head->next becomes the current value of head, and loop
// release order: ensure new_head->next = cur_head is observed before CAS
while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(new_head->next, new_head,
std::memory_order_release,
std::memory_order_relaxed))
;
}
// paper: GETEL
std::optional<T> pop() {
Node<T> *cur_head;
// paper: L R2, ANCHOR
// read current head
cur_head = head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
// paper: LTR R2, R2; BZ EMPTY
while (cur_head) {
// paper: L R4, ELNEXT-EL(,R2)
// cur_head->next becomes the new list head
Node<T> *new_head = cur_head->next;
// paper: CS R2, R4, ANCHOR
// atomic swap if head == cur_head
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: cur_head becomes the current value of head, and loop
// acquire order: ensure cur_head->data is done after CAS
if (head.compare_exchange_weak(cur_head, new_head,
std::memory_order_acquire,
std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
// success
T result = cur_head->data;
// can we delete here?
// delete cur_head;
return result;
}
}
// no elements
return {};
}
};
在其他的一些 Treiber Stack 实现里,push 内部会写成一个 do-while 循环,在 CAS 失败的时候重新把 new_head->next 设置为 head 的值。这里直接用的无循环体的 while,是利用了 C++ std::atomic 的特性:它的 compare_exchange_weak 在失败的时候,会自动把 head 的值写入到第一个参数内。
生成的 AMD64 汇编指令如下:
tack<int>::push(int const&):
# function prologue
pushq %rbp
movq %rsi, %rbp
pushq %rbx
# rbx = &head
movq %rdi, %rbx
# call operator new to allocate 16 bytes of memory
movl $16, %edi
subq $8, %rsp
call operator new(unsigned long)
# new_head = new (16)
movq %rax, %rdx
# eax = data
movl 0(%rbp), %eax
# new_head->next = nullptr
movq $0, 8(%rdx)
leaq 8(%rdx), %rcx
# new_head->data = data
movl %eax, (%rdx)
# cur_head = head.load()
movq (%rbx), %rax
# new_head->next = cur_head
movq %rax, 8(%rdx)
.L8:
# rax = new_head->next
movq (%rcx), %rax
# compare rax(new_head->next) and head
# if equal: head = new_head
# else: rax = head
lock cmpxchgq %rdx, (%rbx)
# jump to .L9 if swapped
je .L9
# new_head->next = rax
movq %rax, (%rcx)
# try again
jmp .L8
.L9:
addq $8, %rsp
popq %rbx
popq %rbp
ret
Stack<int>::pop():
# cur_head = head.load()
movq (%rdi), %rax
.L12:
testq %rax, %rax
# jump to .L17 if cur_head is null
je .L17
# new_head = cur_head->next
movq 8(%rax), %rdx
# compare rax(cur_head) and head
# if equal: head = new_head
# else: rax = head
lock cmpxchgq %rdx, (%rdi)
# jump to .L12 if not swapped
jne .L12
# result = cur_head->data
movl (%rax), %eax
# return result
movb $1, -4(%rsp)
movl %eax, -8(%rsp)
.L13:
movq -8(%rsp), %rax
ret
.L17:
movq $0, -8(%rsp)
jmp .L13
可见核心就是 lock cmpxchgq reg, mem 指令,它的语义是:
- 比较 mem 指向的内存中的值和 rax 寄存器的值
- 如果相等:ZF=1,把 reg 的值写入到 mem 指向的内容
- 如果不相等:ZF=0,把 mem 指向的内存中的值,写入到 rax 寄存器
并且整个过程是原子的。
在 ARMv8.1-a 上编译,则:
- push 会用 CASL 指令实现 release order 的 64-bit CAS
- pop 会用 CASA 指令实现 acquire order 的 64-bit CAS
CAS{A,L} Xs, Xt, [Xn|SP, #0] 的语义:
- 比较 [Xn|SP, #0] 指向的内存中的值和 Xs 寄存器的值
- 如果相等:把 Xt 的值写入到 [Xn|SP, #0] 指向的内容
- 如果不相等:把 [Xn|SP, #0] 指向的内存中的值,写入到 Xs 寄存器
为了判断是否交换成功,还需要额外的 CMP 指令,判断 Xs 在执行 CAS 指令前后的值是否相同。
ABA 问题以及解决方法
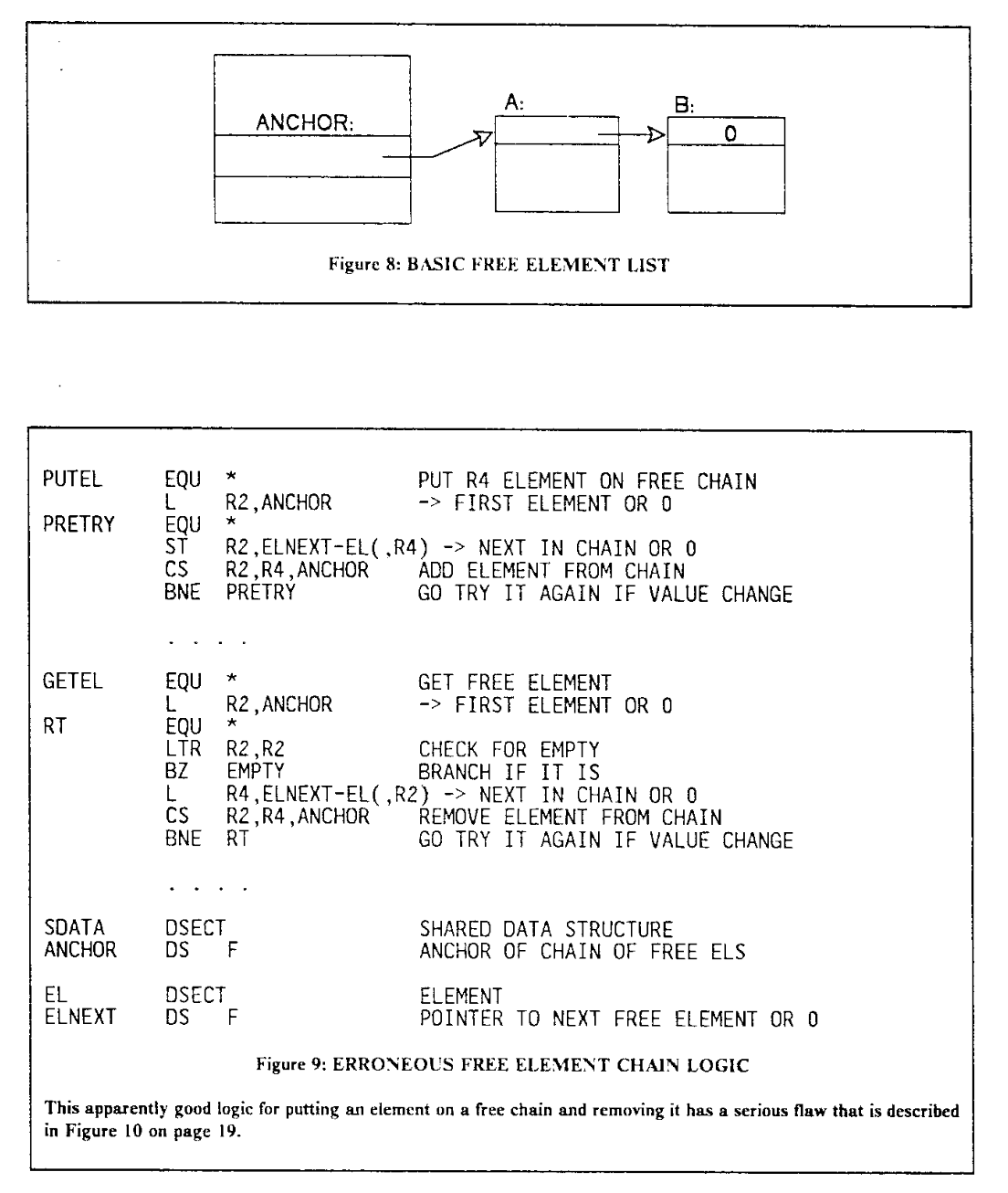
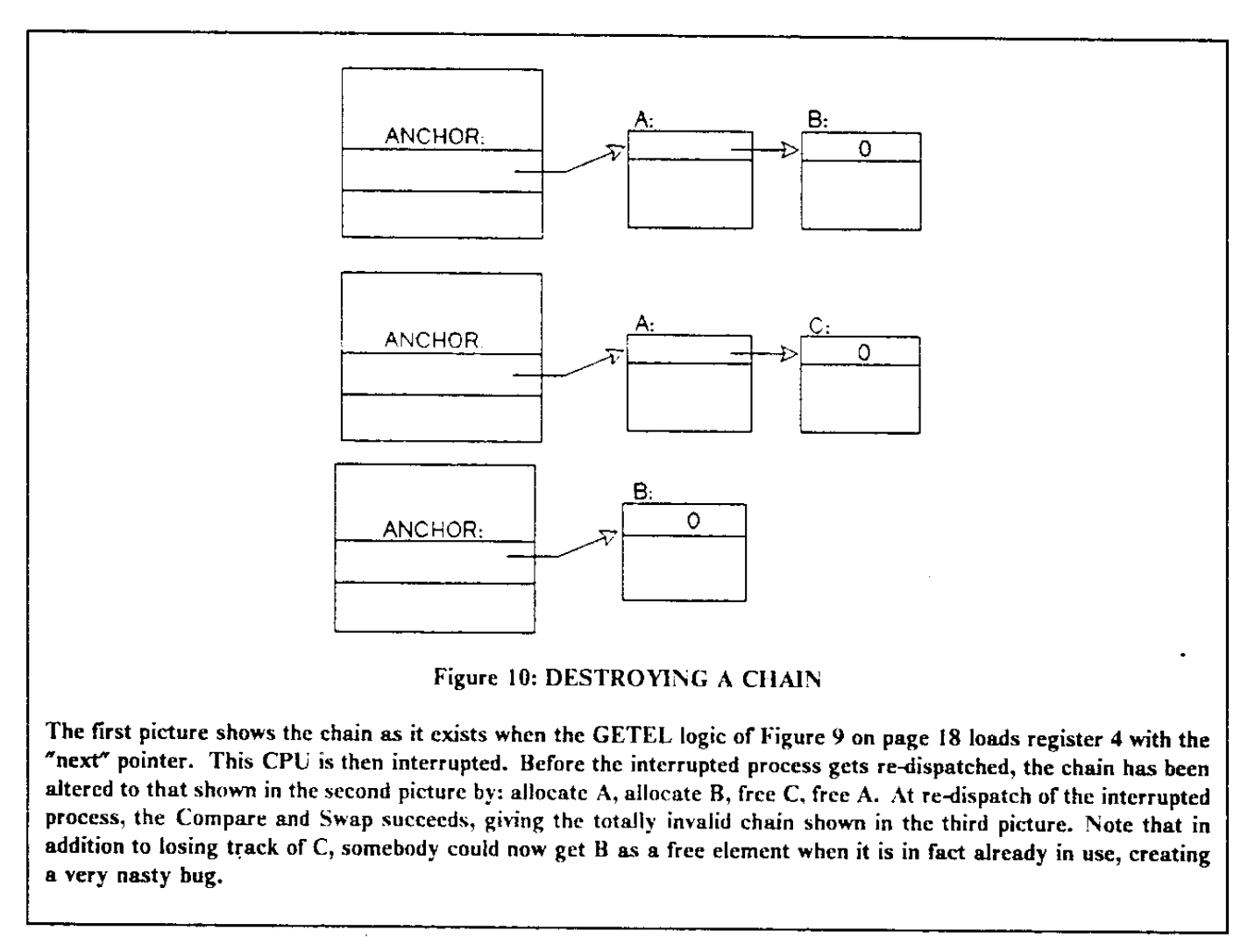
但是这样的实现有一个 ABA 问题(ABA 指某个值从 A 改成 B 再改成 A):CAS 是根据指针的值来判断是否要 swap,但是指针的值不变,不代表指针指向的还是同一个对象。例如 head 指针(下图的 ANCHOR)指向的 node(下图的 A)被 pop 掉了,未来又重新 push,push 的时候恰好 new 出来了同一个指针,就会导致 CAS 写入 next 指针的值用的是原来的 node(下图的 A)的 next(下图的 B),但这个值此时是非法的:
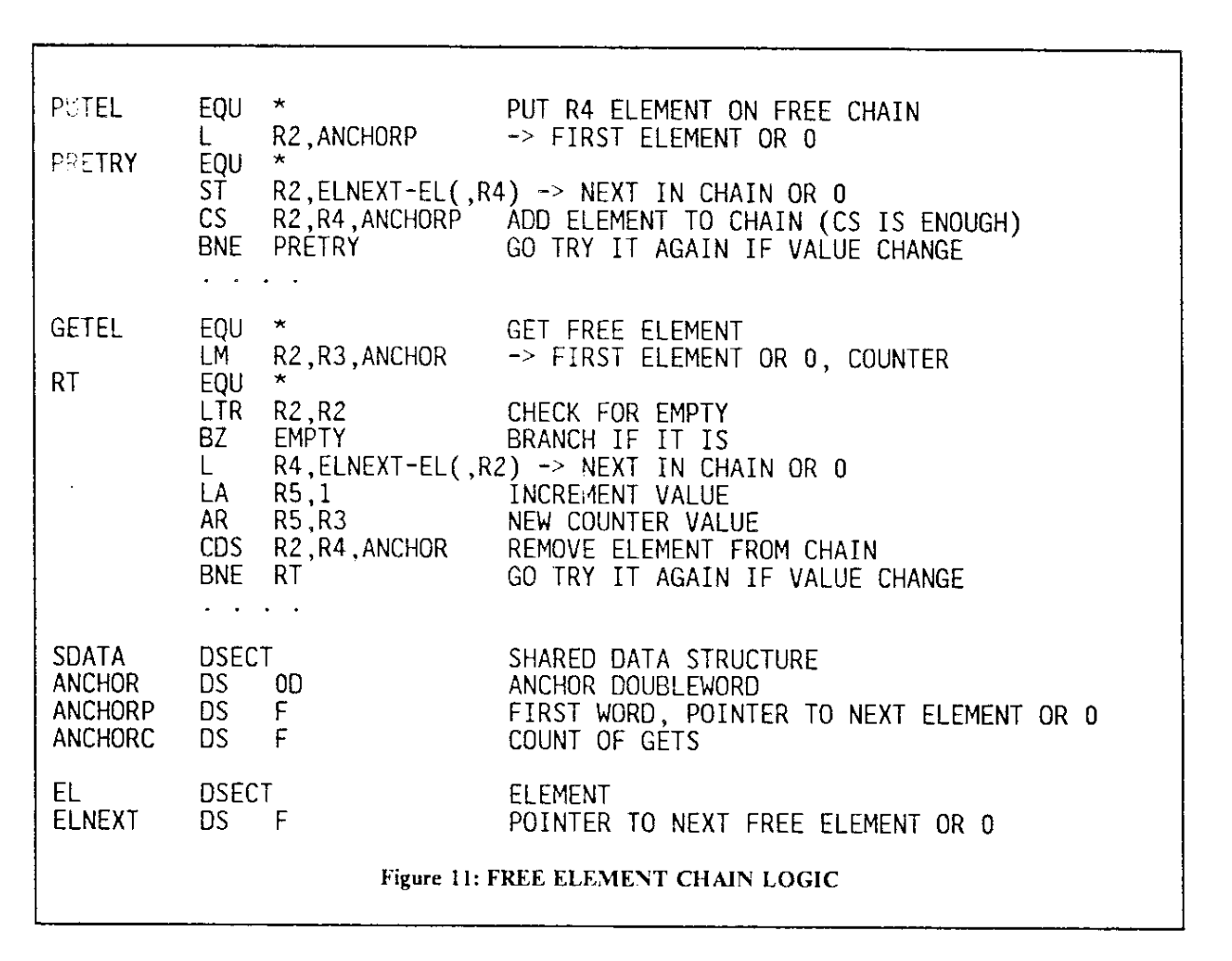
为了解决这个问题,需要把链表头指针和一个整数绑在一起,二者同时 CAS:每次更新指针的时候,就把这个整数加一,这样就可以区分出前后两个 A 指针了,即使它们指针的值相同,但是整数不同,依然可以正常区分。这需要硬件的支持,通常叫做 Double-wide compare and swap,详见 原子指令;如果硬件不支持 Double-wide compare and swap,同时虚拟地址没有占用完整的指针长度(例如 64 位下虚拟地址通常只有 48 位),可以复用指针的高位来保存这个整数。使用 Double-wide compare and swap 的汇编版本:
汇编出现了新的指令:
LM REG1, REG2, MEM:从 MEM 内存读取两个寄存器的数据,到 REG1 和 REG2LA REG, IMM:Load Address,加载立即数 IMM 到 REGAR REG1, REG2:Add Register,两个寄存器相加CDS REG1, REG2, MEM:Compare Double and Swap,把 REG1 和 REG1+1 两个 l 连号的存器作为一个整体,把 REG2 和 REG2+1 两个连号的寄存器作为一个整体,实现一个两倍宽度的 Compare and Swap
对应的 C++ 版本:
#include <atomic>
#include <optional>
template <class T> struct Node {
T data; // user data
Node<T> *next; // pointer to next node
Node(const T &data) : data(data), next(nullptr) {}
};
template <class T> struct HeadWithCounter {
// paper: ANCHORP
// head of singly linked list
Node<T> *head;
// paper: ANCHORC
// allocation counter
size_t counter;
HeadWithCounter() : head(nullptr), counter(0) {}
};
template <class T> struct Stack {
// paper: ANCHOR
// head of singly linked list with counter
std::atomic<HeadWithCounter<T>> head;
Stack() : head(HeadWithCounter<T>()) {}
// paper: PUTEL
void push(const T &data) {
HeadWithCounter<T> new_head;
new_head.head = new Node<T>(data);
// paper: L R2, ANCHORP
// read current head
// in paper, only head pointer is used for CAS;
// it is hard to do so with std::atomic
HeadWithCounter<T> cur_head = head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
do {
// paper: ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4)
// link the new list
new_head.head->next = cur_head.head;
new_head.counter = cur_head.counter;
// paper: CS R2, R4, ANCHOR; ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4) on failure
// atomic swap if head == cur_head
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: cur_head becomes the current value of head, and loop
// release order: ensure write to new_head.head is observed before CAS
} while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(cur_head, new_head,
std::memory_order_release,
std::memory_order_relaxed));
}
// paper: GETEL
std::optional<T> pop() {
HeadWithCounter<T> cur_head;
// paper: LM R2, R3, ANCHOR
// read current head
cur_head = head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
// paper: LTR R2, R2; BZ EMPTY
while (cur_head.head) {
// paper: L R4, ELNEXT-EL(,R2)
// cur_head->next becomes the new list head
HeadWithCounter<T> new_head;
new_head.head = cur_head.head->next;
// paper: LA R5, 1; AR R5, R3
// update counter to handle ABA problem
new_head.counter = cur_head.counter + 1;
// paper: CDS R2, R4, ANCHOR
// atomic swap if head == cur_head
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: cur_head becomes the current value of head, and loop
// acquire order: ensure cur_head->data is read after CAS
if (head.compare_exchange_weak(cur_head, new_head,
std::memory_order_acquire,
std::memory_order_relaxed)) {
// success
T result = cur_head.head->data;
// can we delete here?
// delete cur_head.head;
return result;
}
}
// no elements
return {};
}
};
如果想要在 push 里只 CAS head 指针而不是完整的两倍宽度的 HeadWithCounter,可以用 __atomic builtin:
#define dsize_t unsigned __int128
template <class T> struct Node {
T data; // user data
Node<T> *next; // pointer to next node
Node(const T &data) : data(data), next(nullptr) {}
};
template <class T> struct HeadWithCounter {
union {
dsize_t inner;
struct {
// paper: ANCHORP
// head of singly linked list
Node<T> *head;
// paper: ANCHORC
// allocation counter
size_t counter;
};
};
HeadWithCounter() : head(nullptr), counter(0) {}
};
template <class T> struct Stack : BaseStack<T> {
// paper: ANCHOR
// head of singly linked list with counter
HeadWithCounter<T> head;
Stack() {}
// paper: PUTEL
void push(const T &data) override {
Node<T> *new_head = new Node<T>(data);
// paper: L R2, ANCHORP
// read current head
Node<T> *cur_head = __atomic_load_n(&head.head, __ATOMIC_RELAXED);
// paper: ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4)
// link the new list
new_head->next = cur_head;
// paper: CS R2, R4, ANCHOR; ST R2, ELNEXT-EL(,R4) on failure
// atomic swap if head == new_head->next
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: new_head->next becomes the current value of head, and loop
// release order: ensure new_head->next = cur_head is observed before CAS
while (!__atomic_compare_exchange_n(&head.head, &new_head->next, new_head,
true, __ATOMIC_RELEASE,
__ATOMIC_RELAXED))
;
}
// paper: GETEL
std::optional<T> pop() override {
HeadWithCounter<T> cur_head;
// paper: LM R2, R3, ANCHOR
// read current head
cur_head.inner = __atomic_load_n(&head.inner, __ATOMIC_RELAXED);
// paper: LTR R2, R2; BZ EMPTY
while (cur_head.head) {
// paper: L R4, ELNEXT-EL(,R2)
// cur_head->next becomes the new list head
HeadWithCounter<T> new_head;
new_head.head = cur_head.head->next;
// paper: LA R5, 1; AR R5, R3
// update counter to handle ABA problem
new_head.counter = cur_head.counter + 1;
// paper: CDS R2, R4, ANCHOR
// atomic swap if head == cur_head
// on success: head becomes new_head
// on failure: cur_head becomes the current value of head, and loop
// acquire order: ensure cur_head->data is read after CAS
if (__atomic_compare_exchange_n(&head.inner, &cur_head.inner,
new_head.inner, true, __ATOMIC_ACQUIRE,
__ATOMIC_RELAXED)) {
// success
T result = cur_head.head->data;
// cur_head is leaked, since we cannot reclaim memory immediately
cur_head.head->next = nullptr;
return result;
}
}
// no elements
return {};
}
virtual const char *name() override { return "treiber_stack_v2"; }
};
在 Java 语言版本的 Treiber Stack 中,不会有 ABA 的问题,因为 Java 运行时保证了,CAS 的时候两个不同的对象不会被视为相等。
内存回收问题
但其实,上面的两种实现都有一个问题,就是把 delete 注释掉了,这样其实会导致内存泄漏。假如在 pop 中 delete,会导致什么情况呢:
- 假如两个线程同时进入
pop()函数,并且此时链表的内容是head -> A -> B - 两个线程都获取到了当前的
head的值,记录到了cur_head局部变量当中,这个值等于 A 的地址 - 然后第一个线程完成了 pop 的剩余过程,此时链表的内容是
head -> B,同时delete A - 第二个线程继续执行,尝试读取
cur_head->next,但此时cur_head就是 A,但它已经被释放了,出现了 use after free
可能的解决办法:
- 延迟释放:把要释放的结点放到一个 lock free 的链表当中,然后统计当前正在执行 pop 的线程的个数,当只有当前一个线程在进行 pop,则把链表取下来(CAS 成 null),再释放链表中的结点
- 引用计数:对结点进行引用计数,当引用计数降为零的时候再释放
- Hazard Pointer:见下
Hazard Pointers
Hazard Pointers 是由 M.M.Michael 在 2004 的论文 Hazard Pointers: Safe Memory Reclamation for Lock-Free Objects 中提出的一种方法,可以给很多种 Lock Free 数据结构实现内存的安全回收。
它的思路是:维护一个全局的指针数组,每个线程对应数组里的一项(或若干项,在 Treiber Stack 里只需要一项就足够,因为 pop 只会访问一个结点,也就只需要保护这一个结点),这一项记录了该线程在 pop 函数中正在访问的结点;在释放结点之前,首先要在全局的指针数组里检查它是否被其他的线程访问:如果是,则放到一个链表中等待释放,直到未来某次检查的时候,发现没有被其他线程访问为止;如果否,则可以立即释放。
检查要释放的结点是否在全局的指针数组中,并回收那些可以释放的结点的过程如下:
图中 head 维护了各个线程的信息的链表,其中 HP 数组就是记录了各个线程正在访问的 Hazard Pointers;rlist 就是等待被释放的结点,如果它不在任何一个线程的 HP 当中,就可以释放掉了;否则就继续放在 rlist 里面,等下一次 Scan 再尝试释放。
接下来就是如何维护这些全局的状态:
有了 Hazard Pointers 机制以后,再改写 Treiber Stack 的 pop 函数,就可以实现内存回收了:
Push/Pop Elimination 消除
虽然 Treiber Stack 实现了 Lock free 的 Push 和 Pop 操作,但由于每次都是操作的同一个指针,导致实际上更新是串行的,性能受限。为了解决这个问题,可以引入 Elimination:即给 Push 和 Pop 进行配对,如果发现两个线程分别在进行 Push 和 Pop,那就把 Push 的数据传递给 Pop,然后就不需要更新 Stack 了。为了实现这个配对,需要引入额外的 Elimination Array。这个方法由 Danny Hendler、Nir Shavit 和 Lena Yerushalmi 在 2004 年的论文 A scalable lock-free stack algorithm 中提出,具体地:
- Push/Pop 的时候,首先按照 Treiber Stack 的方式进行 CAS,如果 CAS 成功,那就直接结束;如果 CAS 失败,不立即重试,而是尝试进行一次 Elimination
- 尝试 Eliminate:在一个 Elimination Array 当中,随机选取一项,根据它的占用状态:
- 如果没有其他线程在占用,那就由本线程占用这一项,然后等待一段时间,直到有其他线程来访问同一项
- 如果已经有其他线程占用了这一项,并且本线程和占用了这一项的现场正好是一 Push 一 Pop,就进行 Eliminate
- 如果 Eliminate 失败,回到 Treiber Stack 的方式,重新进行 CAS
参考
- Systems Programming: Coping With Parallelism
- Treiber stack
- A Lock-Free Stack: A Complete Implementation
- Hazard Pointers: Safe Memory Reclamation for Lock-Free Objects
Queue
在 The Art of Multiprocessor Programming 的 10.5 An Unbounded Lock-Free Queue 中描述了一种 Lock Free 的 Queue 实现,它支持 enqueue 和 dequeue 两个操作。这个算法来自论文 Simple, fast, and practical non-blocking and blocking concurrent queue algorithms,由 Maged M. Michael 和 Michael L. Scott 在 1996 年提出。论文中的实现如下:
其 Java 实现如下:
// from The Art of Multiprocessor Programming Figure 10.9 to 10.11
public class Node {
public T value;
public AtomicReference<Node> next;
public Node(T value) {
this.value = value;
next = new AtomicReference<Node>(null);
}
}
public class LockFreeQueue<T> {
private AtomicReference<Node> head;
private AtomicReference<Node> tail;
public void enq(T value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
while (true) {
Node last = tail.get();
Node next = last.next.get();
if (last == tail.get()) {
if (next == null) {
if (last.next.compareAndSet(next, node)) {
tail.compareAndSet(last, node);
return;
}
} else {
tail.compareAndSet(last, next);
}
}
}
}
public T deq() throws EmptyException {
while (true) {
Node first = head.get();
Node last = tail.get();
Node next = first.next.get();
if (first == head.get()) {
if (first == last) {
if (next == null) {
throw new EmptyException();
}
tail.compareAndSet(last, next);
} else {
T value = next.value;
if (head.compareAndSet(first, next))
return value;
}
}
}
}
}
Java 版本和论文的实现有两点不同:
- CAS 没有加 counter,因为 Java 保证了不同对象的比较不会相等
- 去掉了显式的 free,而是交给垃圾回收
Set
在 The Art of Multiprocessor Programming 的 9.8 Non-Blocking Synchronization 中描述了一种 Lock Free 的 Set 实现,它支持 add、remove 和 contains 三个操作,它的实现方式是把 Set 的元素按照 key 从小到大放置在一个链表当中(List-based set)。这个算法由 Maged M. Michael 在 2002 年的论文 High performance dynamic lock-free hash tables and list-based sets 中提出。论文中的实现如下:
其 Java 实现如下:
// from The Art of Multiprocessor Programming
class Window {
public Node pred, curr;
Window(Node myPred, Node myCurr) {
pred = myPred;
curr = myCurr;
}
}
public Window find(Node head, int key) {
Node pred = null, curr = null, succ = null;
boolean[] marked = {false};
boolean snip;
retry:
while (true) {
pred = head;
curr = pred.next.getReference();
while (true) {
succ = curr.next.get(marked);
while (marked[0]) {
snip = pred.next.compareAndSet(curr, succ, false, false);
if (!snip)
continue retry;
curr = succ;
succ = curr.next.get(marked);
}
if (curr.key >= key)
return new Window(pred, curr);
pred = curr;
curr = succ;
}
}
}
public boolean add(T item) {
int key = item.hashCode();
while (true) {
Window window = find(head, key);
Node pred = window.pred, curr = window.curr;
if (curr.key == key) {
return false;
} else {
Node node = new Node(item);
node.next = new AtomicMarkableReference(curr, false);
if (pred.next.compareAndSet(curr, node, false, false)) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
public boolean remove(T item) {
int key = item.hashCode();
boolean snip;
while (true) {
Window window = find(head, key);
Node pred = window.pred, curr = window.curr;
if (curr.key != key) {
return false;
} else {
Node succ = curr.next.getReference();
snip = curr.next.compareAndSet(succ, succ, false, true);
if (!snip)
continue;
pred.next.compareAndSet(curr, succ, false, false);
return true;
}
}
}
public boolean contains(T item) {
boolean[] marked = false;
int key = item.hashCode();
Node curr = head;
while (curr.key < key) {
curr = curr.next.getReference();
Node succ = curr.next.get(marked);
}
return (curr.key == key && !marked[0])
}
为了解决链表的并发修改问题,它给每个结点添加了一个 marked 属性,当这个结点要被删除的时候,先不把它从链表中删掉,而是打上标记;之后在遍历的时候,再把要删除的结点从链表中删除并回收。
Lock Free vs Wait Free
根据 The Art of Multiprocessor Programming:
- A method is wait-free if it guarantees that every call finishes in a finite number of steps.
- A method is lock-free if it guarantees that some call always finishes in a finite number of steps.
Wait free 更强,要求所有调用都可以在有限步内完成;Lock free 强调的是整个系统一直在工作,总有调用可以在有限步内完成。在 Treiber Stack 里,push 和 pop 都有 while(true) 循环,如果线程 A 一直在调用 push/pop,那么线程 B 的 push/pop 调用可能一直无法成功,此时不能保证 Wait free,但是两个线程至少有一个是在操作 Treiber Stack 的,所以是 Lock free。
推荐阅读
- An Introduction to Lock-Free Programming
- Lockless Programming Considerations for Xbox 360 and Microsoft Windows
- Lock-Free Programming by Geoff Langdale